Driven by many research projects worked on over the past years, my past and current work have many “data-driven” components. I worked on many examples of research output that fit the dimensions of descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive analytics. Data-driven logistics research is becoming increasingly important following ever-growing rich datasets. I will build more extensively upon this evolution. An OECD report discusses the Data-Driven Innovation (DDI) cycle in detail. DDI is described as a sequence of phases from datafication to data analytics and decision-making.
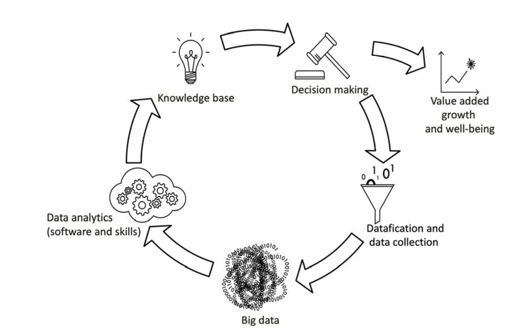
Datafication and data collection involve data generation through digitizing content and monitoring activities. The result of datafication and data collection can be seen as “Big Data”. This last must be exploited through advanced data analytics, visualization, analysis, etc. Over time, a knowledge base evolves, i.e., the state of the learning system (e.g., machine learning). The value of big data and the knowledge base is explicitly exploited through decision-making (actions). Decisions taken, in turn, lead to more or different data and are the start of a new cycle.
Within this described framework, my future research focus will be more and more on the interface between the knowledge base and decision-making or on the prescriptive analytics dimension. Understanding, applying, and optimizing this connection between data/information and decision-making is a fascinating research area, mainly applied to freight transport, logistics, and mobility.
A few interesting papers that could be looked into are:
- Florio, A., J. Kinable, T. Van Woensel, Learning Time-Dependent Travel Speeds from Big Data
- Galiulina, A., N. Mutlu, J. Kinable, T. Van Woensel, Demand steering in a last-mile delivery problem with multiple delivery channels
- Ozarik, S.S., L.P. Veelenturf, T. Van Woensel, G. Laporte (2021), Optimizing last-mile e-commerce deliveries under uncertain customer presence, Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 148, 36 p., 102263
- Lurkin V., J. Hambuckers and T. Van Woensel (2021), Urban Low Emissions Zones: An Operations Management Perspective, Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 144, 222-240
- Tikani H., R. Ramezanian, M. Setak, T. Van Woensel (2020), Hybrid evolutionary algorithms and Lagrangian relaxation for multi-period star hub median problem considering financial and service quality issues, Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 97, 104056
- Jiang J., N. Dellaert, T. Van Woensel and L. Wu (2019), Modeling Traffic Flows and Estimating Road Travel Times in Transportation Network under Dynamic Disturbances, Transportation, 47, 6, pp. 2951-2980
- Van Donselaar K., V. Gaur, T. Van Woensel, R.A.C.M. Broekmeulen, J.C. Fransoo (2010), Ordering Behavior in Retail Stores and Implications for Automated Ordering, Management Science, Volume: 56, Issue: 5, Pages: 766-784
- Data-Driven Innovation: Big Data for Growth and Well-Being, OECD Publishing, Paris. http://dx.doi.org/10.1787/9789264229358-en